Let's break down quantum computing into simpler terms and use some examples to make it easier to understand.
What is Quantum Computing?
1. Classical Computers:
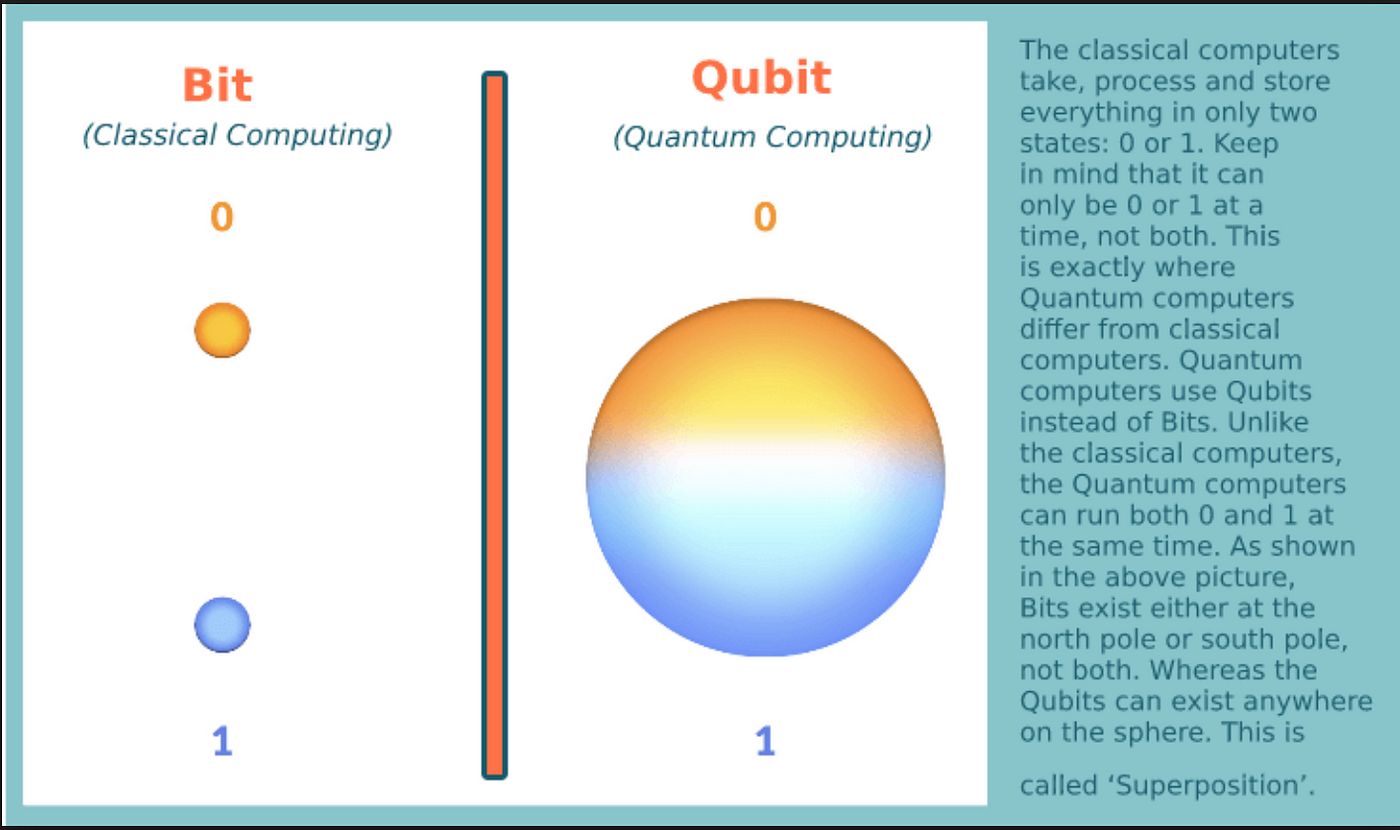
These are the regular computers we use every day, like laptops and smartphones. They process information using bits, which can be either 0 or 1.
2. Quantum Computers:
These use quantum bits, or qubits, which can be 0, 1, or both at the same time due to a property called superposition. This allows quantum computers to process much more information simultaneously.
Key Concepts
1. Superposition:
In classical computing, a bit is either 0 or 1. In quantum computing, a qubit can be 0, 1, or both 0 and 1 at the same time. This is like spinning a coin: it's not just heads or tails but can be in a state that represents both.
2. Entanglement:
Qubits can be entangled, meaning the state of one qubit is directly related to the state of another, no matter how far apart they are. It's like having two magic dice: if you roll one and it lands on a 3, the other one will automatically land on a 3 too.
3. Interference:
Quantum computers use interference to amplify the right answers and cancel out the wrong ones. Think of it like waves in the ocean: when waves align, they create a bigger wave; when they are out of sync, they cancel each other out.
Examples
1. Searching a Database:
Imagine you have a huge phone book with a million names, and you want to find a specific phone number. A classical computer would check each name one by one, which could take a long time. A quantum computer, using superposition, can check all names at once and find the number much faster.
2. Solving Complex Problems:
For tasks like simulating molecules for drug discovery or solving complex optimization problems, quantum computers can process many possibilities simultaneously. This can potentially lead to breakthroughs in medicine and materials science.
3. Encryption and Security:
Quantum computers can factor large numbers much faster than classical computers. This has implications for encryption, as many current security systems rely on the difficulty of factoring large numbers. Quantum computers could break these systems, but they also have the potential to create new, more secure encryption methods.
In the Meme Time... 😉

Simple Analogy
Think of a classical computer as a very fast and efficient librarian who can search through a library one book at a time. A quantum computer is like a magical librarian who can open and read all the books in the library simultaneously, instantly finding the information you need.
Conclusion
Quantum computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in fundamentally different ways compared to classical computing. While still in early development, it holds the promise of solving certain types of problems much more efficiently.
Enjoyed? Share this article with your friends.
For updates, news, fun and games follow us on -
Instagram - BuzzWorthy_O
Twitter - BuzzWorthy_O
Threads - BuzzWorthy_O
Facebook - BuzzWorthy Official
Got queries? Feel free to contact us via -
Gmail - buzzworthy.sv@gmail.com
BuzzWorthy - Contact Us Page
-- Buzzzz 🌸🐝 --



